Article Info
Year: 2025
Month: January
Issue: 1
Pages: 8-9
Key Message: This report thoroughly assesses the colorectal cancer (CRC) screening program in Saudi Arabia from 2021 to 2023. Evidence shows substantial enhancements in the extent of screening coverage, rates of engagement, and adherence to follow-up protocols while highlighting significant variations based on geographical location and gender.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide and is increasing in developing countries[1]. It constitutes 10% of all cancer diagnoses[2]. Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the predominant form of cancer among men and ranks as the third most prevalent cancer among women in Saudi Arabia[3]. Colorectal cancer (CRC) can be detected early with colonoscopy and FIT[4]. Saudi Arabia started a colorectal cancer screening program in 2017 to study its causes and dangers[5]. The program targets symptom-free 45-75-year-olds without polyps or family history. Polyps, first-degree relatives, many second-degree relatives, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, and others are risk factors[3,6]. Analysis of participation and performance measures assessed the national CRC screening program's efficacy and improvement potential.
A retrospective cross-sectional design was utilized to analyze data from the nationwide CRC screening campaign for adults aged 45–75. This helped us gain crucial insights and draw important conclusions. The Cancer Control Program (CCP) and General Administration of Health Programs and Chronic Diseases provided secondary datasets. Fecal immunochemical assays (FIT) and colonoscopies were performed on positive or high-risk patients. Coverage, participation, FIT positive, colonoscopy referral, and compliance rates were investigated meticulously.
The study indicated significant enhancements in many crucial performance metrics across the three-year duration. The coverage rate rose significantly, from 1% in 2021 to 3.4% in 2023 (p < 0.001). The number of persons examined increased substantially from 30,641 in 2021 to 100,340 in 2023 (p < 0.001). Although the FIT positivity rate remained consistent at about 5.7%, there was a substantial rise in the total number of positive FIT readings (p < 0.001). The referral rate for colonoscopy was continuously high, and adherence to colonoscopy sessions showed significant improvement, increasing from 30% in 2021 to 51.2% in 2023 (p < 0.001). Gender and geographical discrepancies were apparent, with a small majority of female participants (51.5%) and notable variances in screening outcomes across different locations.
Colorectal cancer screening was performed in Saudi Arabia from 2021 to 2023. Performance measures improved, with 45-75-year-old screening rates and overall screenings rising. Fecal immunochemical test positivity was maintained at 5.7%. The program's success is evidenced by its high referral rate and therapy adherence. Females constituted 51.5% of the total population. The majority of individuals fell within the age range of 45 to 64. In contrast, men exhibited greater susceptibility. The study highlights the importance of ongoing monitoring and tailored interventions to decrease the incidence of colorectal cancer in Saudi Arabia. Additionally, it fosters disparities between regions and facilitates the gathering of data.
Research on colorectal cancer screening strives to enhance accuracy, thoroughness, and precision. The recommendation proposes transitioning to primary data sources, thorough information verification, and adopting a prospective longitudinal study design. To provide a more comprehensive explanation of the results, it is important to consider factors such as lifestyle, genetics, and socioeconomic background. Local healthcare resource and infrastructure gaps must be addressed to offer fair and equal screening services. A unique identity for each participant can improve monitoring and long-term results. Data on the cause of death and stage of illness is also needed for early detection and treatment. Beneficial participant feedback can improve program efficacy.
Figure1: Annual Coverage Percentage of CRC Screening in Regions of Saudi Arabia (2021-2023)
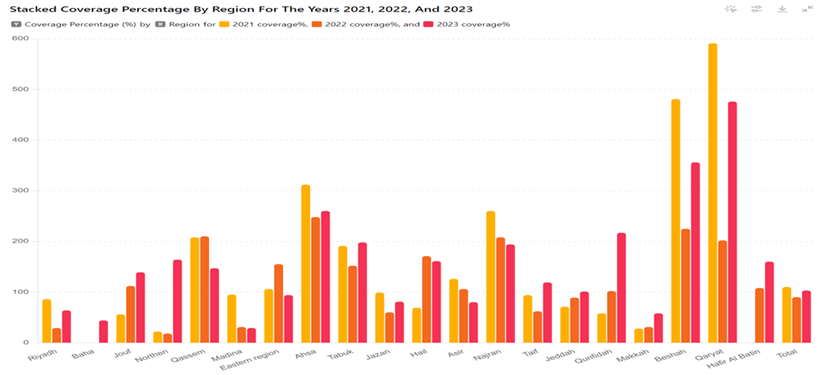
Table 1: Time trends of performance indicators of the colorectal cancer screening program in Saudi Arabia, 2021-2023.
| 2021-2023 | P value | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | Performance indicators |
| - | - | 2713033 | 2768401 | 2796365 | No. of individual eligible for screening |
| 174284 | <0.001 | 92723 | 54357 | 27204 | No. of Invited individual for screening targeted age group only |
| (6.2%) | <0.001 | (3.4%) | (2%) | (1%) | (Coverage rate %) |
| 181764 | <0.001 | 97873 | 55927 | 27964 | No. of Invited individual for screening |
| 181222 | <0.001 | 100340 | 50241 | 30641 | No. of individual screened |
| 173742 | <0.001 | 95190 | 48671 | 29881 | No. of individual screened from the targeted age group (Saudi from 45-75 years) |
| 7480 | <0.001 | 5150 | 1570 | 760 | No. of individual screened out the targeted age group (Saudi from 45-75 years) |
| 95.6% | <0.001 | 97.3% | 87.0% | 106.9% | Participation rate % |
| 171871 | <0.001 | 93565 | 48469 | 29837 | No. of individual screened by FIT test |
| 9316 | <0.001 | 5335 | 2285 | 1696 | No. of individual with positive FIT test |
| (5.4%) | <0.001 | (5.7%) | (4.7%) | (5.7%) | FIT Positivity (%) |
| 11187 | <0.001 | 6960 | 2487 | 1740 | Total positive screened individual |
| 8960 | <0.001 | 5532 | 1983 | 1445 | No. of individual referred for colonoscopy |
| (80.1 %) | <0.01 | (79.5 %) | (79.7 %) | (83 %) | (Referral rate %) |
| 2706 | <0.001 | 2376 | 253 | 77 | No. of individual with high risk factor |
| (24.2 %) | <0.05 | (34.1 %) | (10.2 %) | (4.4 %) | Individual with high risk factor % |
| 4998 | <0.001 | 3561 | 915 | 522 | No. of individuals having attended a colonoscopy examination |
| (44.7 %) | <0.001 | (51.2 %) | (36.8 %) | (30 %) | (Colonoscopy Compliance %) |
References:
1. Rawla P, Sunkara T, Barsouk A. Epidemiology of colorectal cancer: incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Gastroenterology Review. 2019;14(2):89–103.
2. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021 May 4;71(3):209–49.
3. Elwali NE, Jarrah O, Alzahrani SG, Alharbi MB, Alhejaily AG, Alsharm AA, et al. Colorectal Cancer in Saudi Arabia: The Way Forward. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 Dec 5];24(1):13. Available from: /pmc/articles/PMC10152865/
4. Almadi MA, Basu P. Doing things right and doing the right things: Colorectal cancer screening in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Journal of Gastroenterology. 2023;29(2):67–70.
5. Gosadi IM. National screening programs in Saudi Arabia: Overview, outcomes, and effectiveness. J Infect Public Health. 2019 Sep;12(5):608–14.
6. Aljumah A, Aljebreen A. Policy of screening for colorectal cancer in Saudi Arabia: A prospective analysis. Saudi Journal of Gastroenterology. 2017;23(3):161.
تقييم مؤشرات المشاركة والأداء في برنامج فحص سرطان القولون والمستقيم في المملكة العربية السعودية من 2021 إلى 2023
يقوم هذا التقرير بتقييم شامل لبرنامج فحص سرطان القولون والمستقيم (CRC) في المملكة العربية السعودية من عام 2021 إلى عام 2023. تشير الأدلة إلى تحسينات كبيرة في مدى تغطية الفحص، معدلات المشاركة، والالتزام بالبروتوكولات المتبعة، مع تسليط الضوء على التفاوتات الكبيرة بناءً على الموقع الجغرافي والجنس.
سرطان القولون والمستقيم هو السبب الثالث للوفيات المرتبطة بالسرطان على مستوى العالم، ويزداد في البلدان النامية. يشكل سرطان القولون والمستقيم 10% من جميع حالات تشخيص السرطان. يعتبر سرطان القولون والمستقيم الشكل السائد للسرطان بين الرجال ويحتل المرتبة الثالثة بين النساء في المملكة العربية السعودية. يمكن اكتشاف سرطان القولون والمستقيم مبكرًا من خلال تنظير القولون واختبار، بدأت المملكة العربية السعودية برنامج فحص سرطان القولون والمستقيم في عام 2017 لدراسة أسبابه ومخاطره. يستهدف البرنامج الأفراد الذين تتراوح أعمارهم بين 45 و75 عامًا والذين لا يعانون من أعراض وليس لديهم تاريخ عائلي من الأورام الحميدة أو السرطان. تعتبر الأورام الحميدة، الأقارب من الدرجة الأولى، العديد من الأقارب من الدرجة الثانية، التهاب القولون التقرحي، مرض كرون، وغيرها من العوامل عوامل خطر. يهدف تحليل مؤشرات المشاركة والأداء إلى تقييم فعالية البرنامج الوطني لفحص سرطان القولون والمستقيم وإمكانيات تحسينه.
تم استخدام تصميم مقطعي استعادي لتحليل بيانات حملة الفحص الوطنية لسرطان القولون والمستقيم للبالغين الذين تتراوح أعمارهم بين 45 و75 عامًا. ساعدنا هذا في الحصول على رؤى حاسمة واستخلاص استنتاجات مهمة. قدم برنامج مكافحة السرطان والإدارة العامة للبرامج الصحية والأمراض المزمنة مجموعات البيانات الثانوية. تم إجراء اختبارات المناعية الكيميائية البرازية (FIT) وتنظير القولون على المرضى الإيجابيين أو المعرضين لمخاطر عالية. تم التحقيق بدقة في معدلات التغطية، والمشاركة، وإيجابية FIT، والإحالة لمنظار القولون، وعمل المنظار التشخيصي.
أشارت الدراسة إلى تحسينات كبيرة في العديد من مقاييس الأداء الرئيسية خلال فترة الثلاث سنوات. ارتفع معدل التغطية بشكل كبير، من 1% في عام 2021 إلى 3.4% في عام 2023 (p < 0.001). زاد عدد الأشخاص الذين تم فحصهم بشكل كبير من 30,641 في عام 2021 إلى 100,340 في عام 2023 (p < 0.001). على الرغم من أن معدل إيجابية FIT ظل ثابتًا عند حوالي 5.7%، كان هناك ارتفاع كبير في إجمالي عدد قراءات FIT الإيجابية (p < 0.001). كان معدل الإحالة لمنظار القولون مرتفعًا باستمرار، وأظهر الالتزام بجلسات منظار القولون تحسنًا كبيرًا، حيث ارتفع من 30% في عام 2021 إلى 51.2% في عام 2023 (p < 0.001). كانت هناك اختلافات بين الجنسين والجغرافية واضحة، مع أغلبية طفيفة من المشاركين من الإناث (51.5%) وتباينات ملحوظة في نتائج الفحص عبر مواقع مختلفة.
تم إجراء فحص سرطان القولون والمستقيم في المملكة العربية السعودية من عام 2021 إلى عام 2023. تحسنت مقاييس الأداء، مع ارتفاع معدلات الفحص للفئة العمرية 45-75 عامًا وزيادة الفحوصات بشكل عام. تم الحفاظ على إيجابية اختبار (FIT) عند 5.7%. يوضح نجاح البرنامج من خلال معدل الإحالة العالي والالتزام بالعلاج. شكلت الإناث 51.5% من إجمالي السكان. كان معظم الأفراد في الفئة العمرية 45 إلى 64 عامًا. بالمقابل، أظهر الرجال قابلية أكبر للإصابة. تسلط الدراسة الضوء على أهمية المراقبة المستمرة والتدخلات المخصصة لتقليل الإصابة بسرطان القولون والمستقيم في المملكة العربية السعودية. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، تعزز الفوارق بين المناطق وتسهل جمع البيانات.
يهدف البحث حول فحص سرطان القولون والمستقيم إلى تحسين الدقة والشمولية. تقترح التوصية الانتقال إلى مصادر البيانات الأولية، والتحقق الدقيق من المعلومات، واعتماد تصميم دراسة طولية استباقية. لتقديم تفسير أكثر شمولية للنتائج، من المهم مراعاة العوامل مثل نمط الحياة، والوراثة، والخلفية الاجتماعية، والاقتصادية. يجب معالجة فجوات الموارد والبنية التحتية في الرعاية الصحية المحلية لتقديم خدمات فحص عادلة ومتساوية. يمكن للهوية الفريدة لكل مشارك تحسين المراقبة والنتائج طويلة المدى. هناك حاجة أيضًا إلى بيانات حول سبب الوفاة ومرحلة المرض للكشف المبكر والعلاج. يمكن أن يحسن تعليقات المشاركين المفيدة من فعالية البرنامج.